Varicose Veins
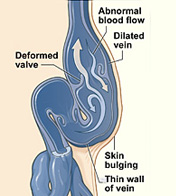
Varicose veins are swollen veins that you can see through your skin. To return blood to your heart, the veins in your legs must work against gravity. Varicose veins may be caused by weakened valves within the veins that allow blood to pool in your veins instead of traveling to your heart. Varicose veins are a common condition and usually cause few signs and symptoms. Sometimes varicose veins cause pain, blood clots, skin ulcers (sores), or other problems. If this happens, your doctor may recommend one or more medical procedures. Some people choose to have these procedures to improve the way their veins look as well.
Symptoms
Some of the symptoms of varicose veins may include:
- Large veins that you can see just under the surface of your skin
- Weight loss
- Mild swelling of your ankles and feet
- Throbbing or cramping in your legs
- Itchy legs, especially on the lower leg and ankle. Sometimes this symptom is incorrectly diagnosed as dry skin
- Discolored skin in the area around the varicose vein
People with significant varicose veins may be at a slightly increased risk of deep venous thrombosis (DVT). DVT may cause unusual and sudden leg swelling, which requires immediate medical attention.
Diagnosis
The physician performs an examination of the legs, noting the texture and color of any prominent veins. A tourniquet or direct hand pressure may be used to observe how a person's veins fill with blood.
To confirm a diagnosis of varicose veins, your physician may recommend these further diagnostic tests:
- Ultrasound: Uses sound waves to measure the speed of blood flow and to allow your doctor to see the structure of your leg veins.
- Angiogram: For this procedure, dye is injected into your veins. The dye outlines your veins on x-ray images. An angiogram can help your doctor confirm whether you have varicose veins or another condition.
Treatment Options
Without treatment, varicose veins tend to worsen. The physician first attempts to treat the symptoms by prescribing non-surgical treatments, such as:
- Leg elevation
- Compression stockings (elastic hosiery)
More extensive or complicated cases of varicose veins may require medical therapy or surgery. Most cases can be treated on an outpatient basis with local anesthetics.
Minimally invasive and surgical treatments may include:
- Sclerotherapy: In sclerotherapy, the physician injects a chemical into the affected veins to cause irritation and scarring inside the vein. This causes the veins to close off and fade away. Sclerotherapy can be done in your doctor's office. You may need several treatments to completely close off a vein.
- Laser Surgery: This procedure applies bursts of light from a laser onto a varicose vein, which makes the vein fade away.
- Endovenous Ablation Therapy: In endovenous ablation your doctor makes a tiny cut in your skin near the varicose vein and inserts a catheter into the vein. A device at the tip of the catheter heats up the inside of the vein and closes it off. The vein is no longer able to carry blood, breaks up, and is reabsorbed by the body. You'll be awake during this procedure, but your doctor will numb the area around the vein. You usually can go home the same day.
- Vein Stripping: Vein stripping and ligation typically is done only for severe cases of varicose veins. In this procedure, the doctor ties shut and removes the veins through small cuts in your skin. You'll be given medicine to temporarily put you to sleep so you don't feel any pain during the procedure. Vein stripping and ligation usually is done as an outpatient procedure.
- Endoscopic Vein Surgery: This operation is usually performed only in advanced cases involving leg ulcers. During the procedure, your doctor uses a tiny camera at the end of a thin tube. It is inserted through small incisions in your leg to move through varicose veins. A surgical device at the end of the camera is used to close the vein. This procedure is performed on an outpatient basis.
- Ambulatory Phlebectomy: During an ambulatory phlebectomy, your doctor will remove small varicose veins through tiny incisions. This procedure usually is done to remove the varicose veins closest to the surface of your skin. You'll be awake during the procedure, but your doctor will numb the area around the vein. Usually, you can go home the same day.
Public domain image(s) provided courtesy of The National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI) http://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health/, part of the National Institutes of Health and the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services.
 Vascular Surgery Specialists
Vascular Surgery Specialists